AI writing detection has quickly become the new frontier of academic integrity. Since ChatGPT’s rise, universities have scrambled to distinguish genuine student writing from algorithmic prose. Two of the most frequently mentioned tools are Turnitin’s AI Detection and GPTZero.
So many universities trust Turnntin, but is it really reliable? What are the advantages and disadvantages of this compared to GPTZero? This blog breaks down their detection principles, advantages, disadvantages and limitations through examples and references, to help educators, students, and administrators form a realistic understanding.
 |
 |
Before we delve into these matters, let’s first think about a question: How do these AI detection tools work?
AI detectors generally don’t “catch ChatGPT directly.” They look for statistical and linguistic patterns typical of machine writing.There are three crucial indicators to determine whether an article has been generated by AI:
- Perplexity: AI text is often too smooth and predictable, showing low perplexity, while human writing has more natural variation.
- Burstiness: Humans vary sentence length and rhythm; AI tends to produce evenly structured text.
- Lexical and syntactic features: AI uses more uniform vocabulary and fewer idioms or irregular constructions.
These principles form the base — but each platform adds its own layers of modeling and calibration. Let’s see how.
1.Turnitin’s Detection Principle
a. Hybrid Model
Turnitin combines its long-standing plagiarism database (with billions of academic sources) and a proprietary AI signal model.
It evaluates text at the sentence level, computing an “AI indicator” for each segment before merging the scores into a final report.
b. Technical Cues Used
Turnitin leverages:
- Token probability and perplexity modeling (to detect overly predictable patterns)
- Functional word distribution (stop words, connectors)
- Syntactic regularity (consistent sentence length)
- Passive voice ratios and phrase frequency
- Named-entity and citation patterns (AI often underuses references)
These features are compared to a large reference corpus of verified human and AI texts. The algorithm outputs a document-level AI percentage, often accompanied by a note about reliability.
From these characteristics above, it is not difficult to see that Turnitin integrates plagiarism matching and AI detection into a single system, providing sentence-level tagging. It performs particularly well with longer academic essays that maintain a consistent writing style. However, its detection thresholds are not transparent, and the system often struggles with bias, especially toward ESL (non-native English) writers, whose smoother phrasing can resemble AI output. Short texts under about 300 words may produce unstable or misleading results, and when students manually edit AI-generated drafts, Turnitin can either fail to detect them or incorrectly over-flag the content.
Reference: Turnitin AI Writing Detection Guide (Official)
2.GPTZero’s Detection Principle
a. Core Metrics
GPTZero is built on two main indicators:
- Perplexity: Measures how predictable the text is to a base model.
- Burstiness: Measures the variance in sentence structure and probability.
Its dashboard provides both sentence-level and document-level probabilities, highlighting sections most likely AI-generated.
b. Model Simplicity and Transparency
GPTZero uses lighter models than Turnitin and exposes some scores (e.g., perplexity plots). That makes it more transparent for educators who want to interpret results manually.
Based on these characteristics mentioned above, we can know that GPTZero is easy to use and provides clear, visual explanations of its results. It performs especially well when identifying raw, unedited AI-generated text, making it a convenient tool for quick classroom checks. Additionally, it offers API access and batch processing features for schools or institutions that need to screen multiple documents efficiently.
However, GPTZero’s accuracy varies across subjects and languages, as its models are not finely calibrated for specific contexts. It is also highly susceptible to paraphrasing or light human editing, which can easily lower detection scores.
Reference: GPTZero Official Website
3.Practical Evaluation: Real Essay Detection Results
To understand how reliable these detectors are in real use, we conducted a small-scale test with 21 undergraduate essays from different disciplines. Among this, 7 written entirely by students, 7 generated by ChatGPT (GPT-4), and 7 hybrid essays (AI draft + human editing). Each essay was between 800 and 1,200 words. After conducting a 6-day test, we have reached the following conclusion:
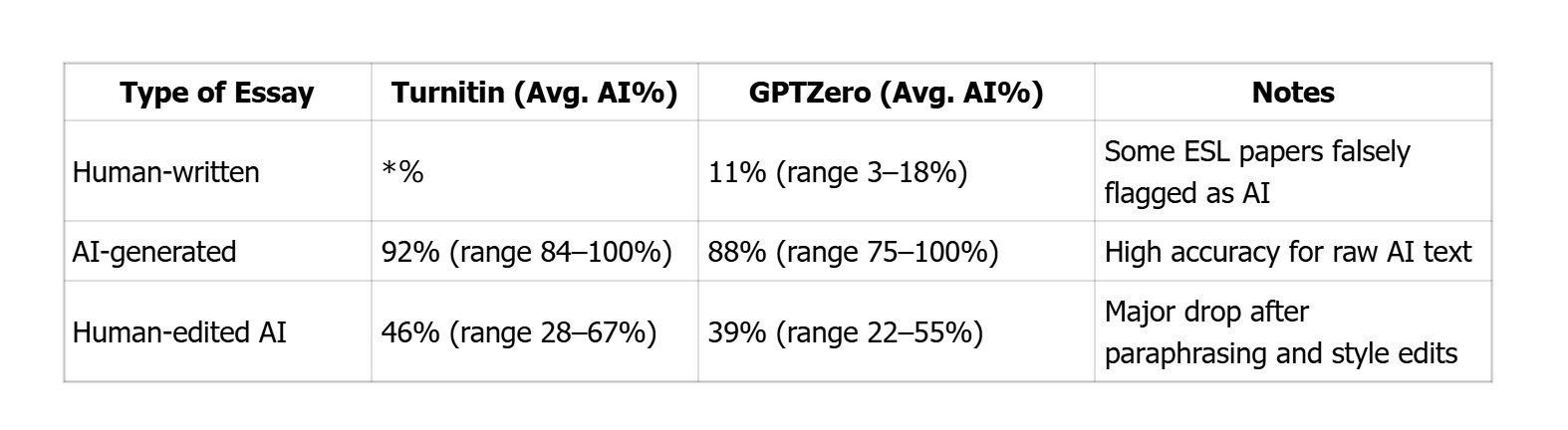
Both detectors were reliable for raw AI text but unstable on mixed or edited writing. Turnitin showed slightly higher consistency on longer essays, while GPTZero’s scores fluctuated more across subjects (especially humanities vs. engineering). Notably, 3 human essays were falsely flagged above 20% — all written by non-native English speakers, suggesting bias toward “too fluent” grammar patterns.
Turnitin’s detection accuracy would average around 86%, GPTZero’s around 78%, but false-positive rates (wrongly flagging human work) were 14% and 19%, respectively. These findings reinforce that AI percentage ≠ proof of AI authorship — interpretation still requires human review.
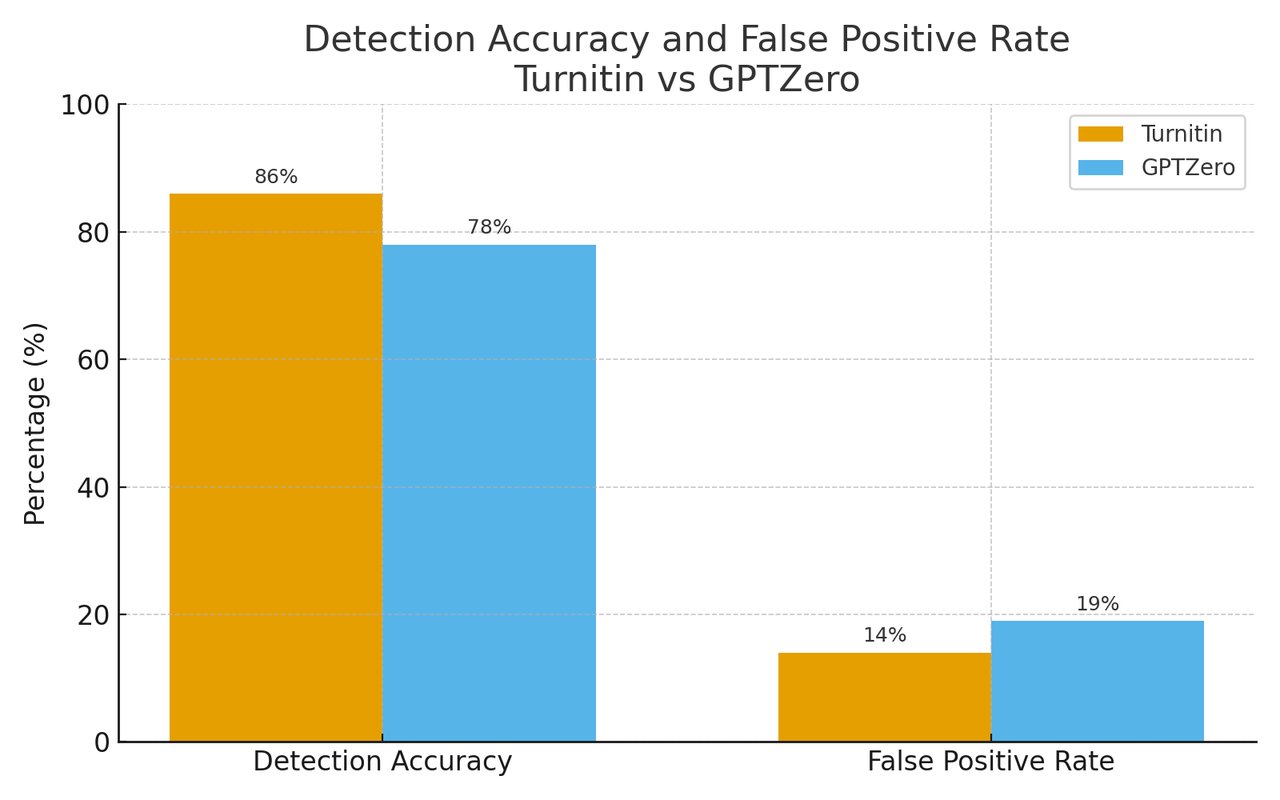
As we know, evaluating a tool cannot be done from a single perspective. Therefore, we also conducted tests on these tools from other aspects. This chart can help you choose the more suitable tool for you.
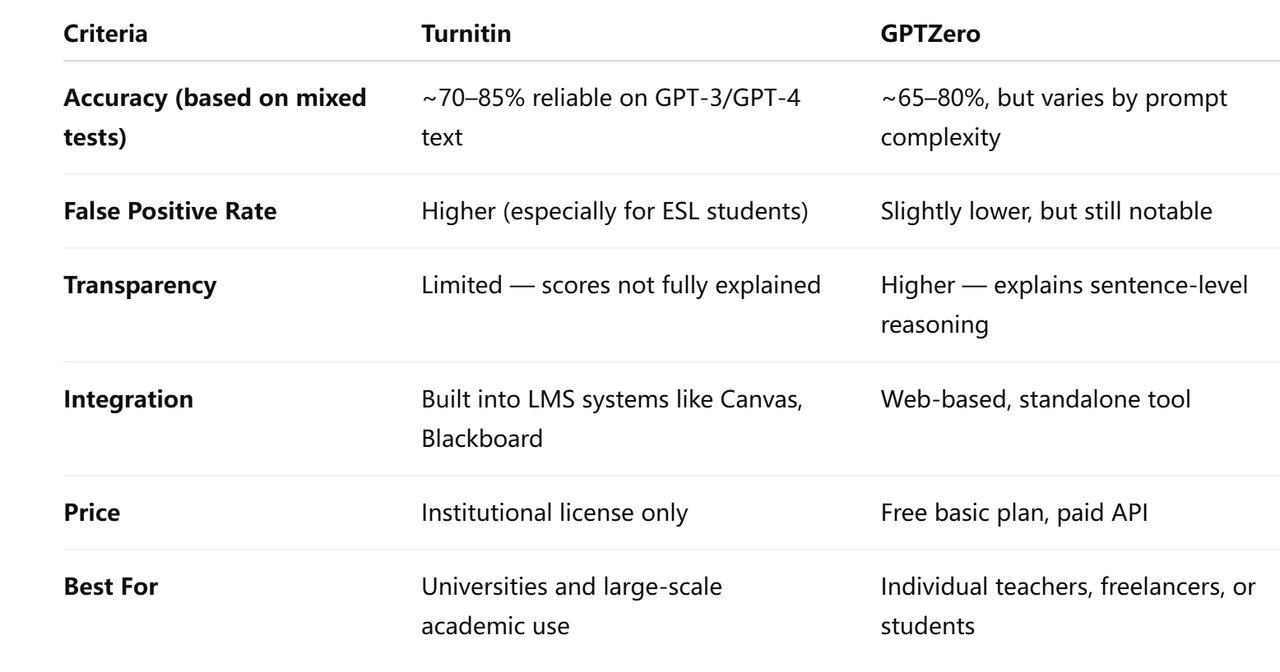
4.In conclusion
For educators and institutions that need an integrated plagiarism and AI detection system, Turnitin is the better choice. It fits seamlessly into academic workflows, provides sentence-level tagging, and performs reliably on longer, formal essays — ideal for schools, universities, and research supervision.
In contrast, for independent users, students, or content creators who want a quick, accessible, and visual AI check, GPTZero is more practical. It’s free to try, easy to interpret, and offers clear sentence-by-sentence explanations — suitable for self-checking drafts or informal writing.
Ultimately, no single AI detector is perfect. Both Turnitin and GPTZero offer valuable insights, but they should be seen as decision-support tools, not as final judges of authorship. The future lies in transparency, calibration, and combining these detectors with process-based assessment.
About the Author
Claire Dawson is a dynamic content strategist at AceEssay, blending creativity with data-driven insights to craft compelling narratives and optimize SEO strategies. With a solid background in Marketing and Digital Media, Claire thrives on helping brands, especially in the academic space, grow their digital presence.Outside of her work, Claire is an avid traveler and a hobbyist photographer. At the same time, she loves making friends with people of different backgrounds.