Recently, we’ve been hearing the same frustration over and over from international students:“I used ChatGPT to polish my essay, but Turnitin flagged 70% as AI.” or“My professor told me my paragraphs sound too ‘machine-like’.” …..I believe that you, who are reading this blog, have also experienced something similar. These aren’t isolated cases!
As Turnitin’s AI detection becomes standard in nearly every university submission system(a built-in feature that analyzes linguistic patterns to identify text likely written by AI), even light edits from ChatGPT can trigger “AI-generated” alerts. Turnitin has also been actively monitoring “AI bypassers” ,and continually updates its algorithms to catch unnatural linguistic patterns.
To understand what really works in 2026, we ran a real-world test of the best AI humanizer tools — comparing how effectively they make text sound natural and pass academic AI detectors like Turnitin and GPTZero.
What Students Care About Most?
After analyzing over 3,127 survey responses from international students in Arts, Social Sciences, and Business courses, we found that users’ biggest concerns about AI writing and “AI humanizer” tools cluster around five main points:
- Natural language flow — The rewritten text must sound human, not “edited by a robot.”
- Academic integrity — The tool shouldn’t destroy logic, citations, or tone.
- AI detection safety — It should lower AI percentage in Turnitin and GPTZero.
- Affordability — Most students expect < $20/month plans.
- Ease of use & multilingual support — Many users write in English as a second language.
These five factors shaped the evaluation criteria for our 2026 tests.
How We Tested?
Last tested: February 2026
Target group: Arts, Social Science, and Business students
Tools tested: We have selected eleven tools that are currently the most popular and have the greatest potential in the market. They are: Undetectable AI, Ace Essay, StealthWriter, QuillBot, HumanizeAI Pro, WalterWrites, Humbot, BypassGPT, Phrasly, Decopy, Humanize.io
AI Detectors used: Turnitin, GPTZero
We relied on two of the most trusted AI detection systems:
- Turnitin —Most universities have integrated Turnitin’s AI writing detection tool into their assessment processes to evaluate academic submissions.The company has also addressed the rise of “AI bypassers” in its official blog, emphasizing continuous model updates to catch unnatural language structures that mimic human writing(Turnitin Blog: What Are AI Bypassers and Why Educators Should Care).
- GPTZero — a popular open-access detector among students and editors. It provides transparent scoring and sentence-level explanations, helping us measure linguistic naturalness more objectively.
Using both allows for a balanced assessment,helping us to obtain a more accurate result.
For this comparison, each tool was tested using the same 500-word excerpt from an AI-written essay on “Cultural Identity and Media Representation”
The text was first written in ChatGPT, then “humanized” using each tool.
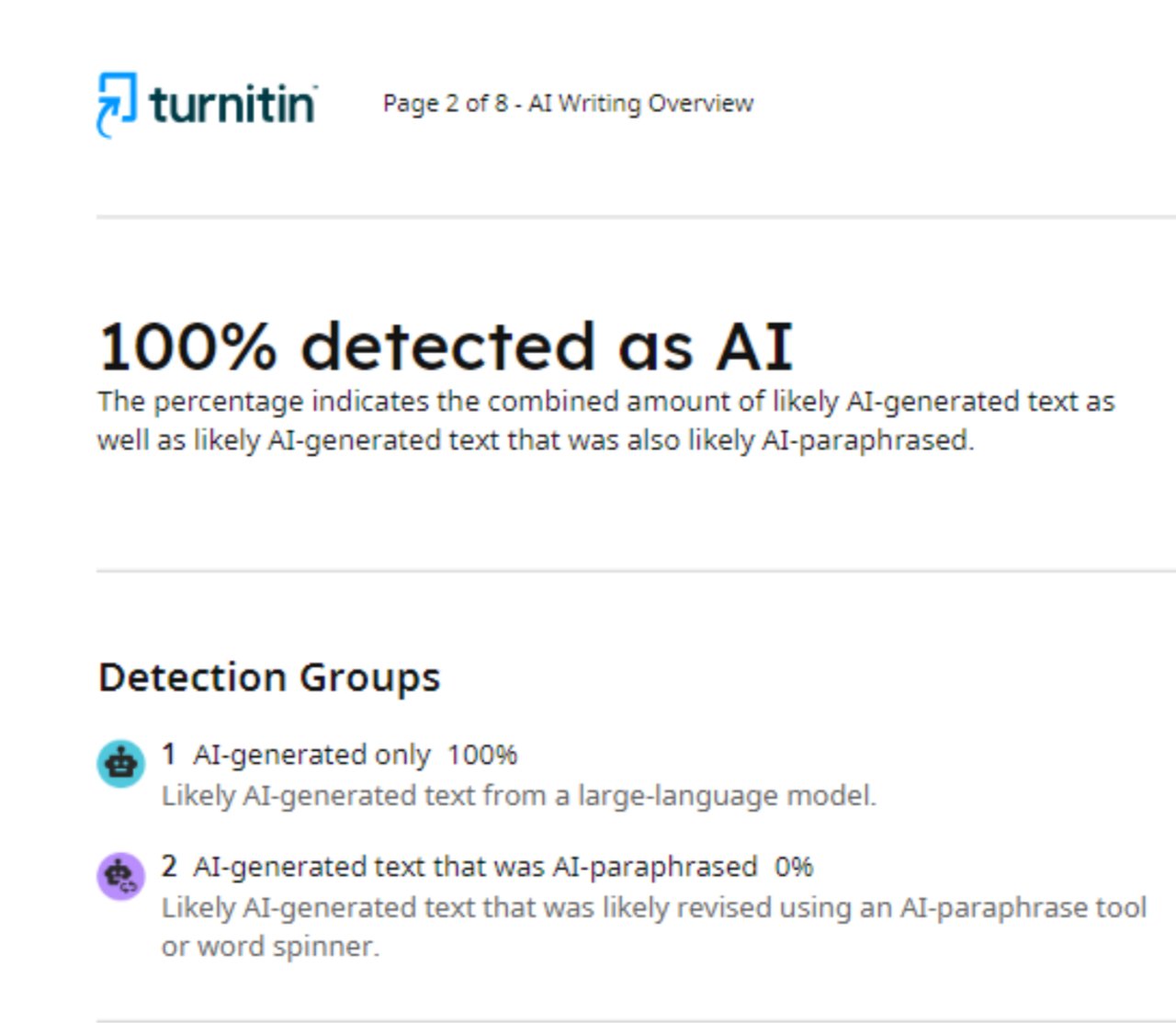
We rated:
- Naturalness (1–10) — judged by 3 academic writing tutors.
- Academic Coherence (1–10) — logical flow, vocabulary precision, tone consistency.
- AI Detection Rate — measured by Turnitin + GPTZero.
- Cost— per-word or monthly plan.
- Ease of Use — processing speed, clarity of output.
OK! After making all the preparations, now let’s officially move on to the evaluation stage.
Tool-by-Tool Evaluation
After a 10-day evaluation process, I compiled this table. Next, I will provide you with a detailed explanation of the advantages and disadvantages of each tool.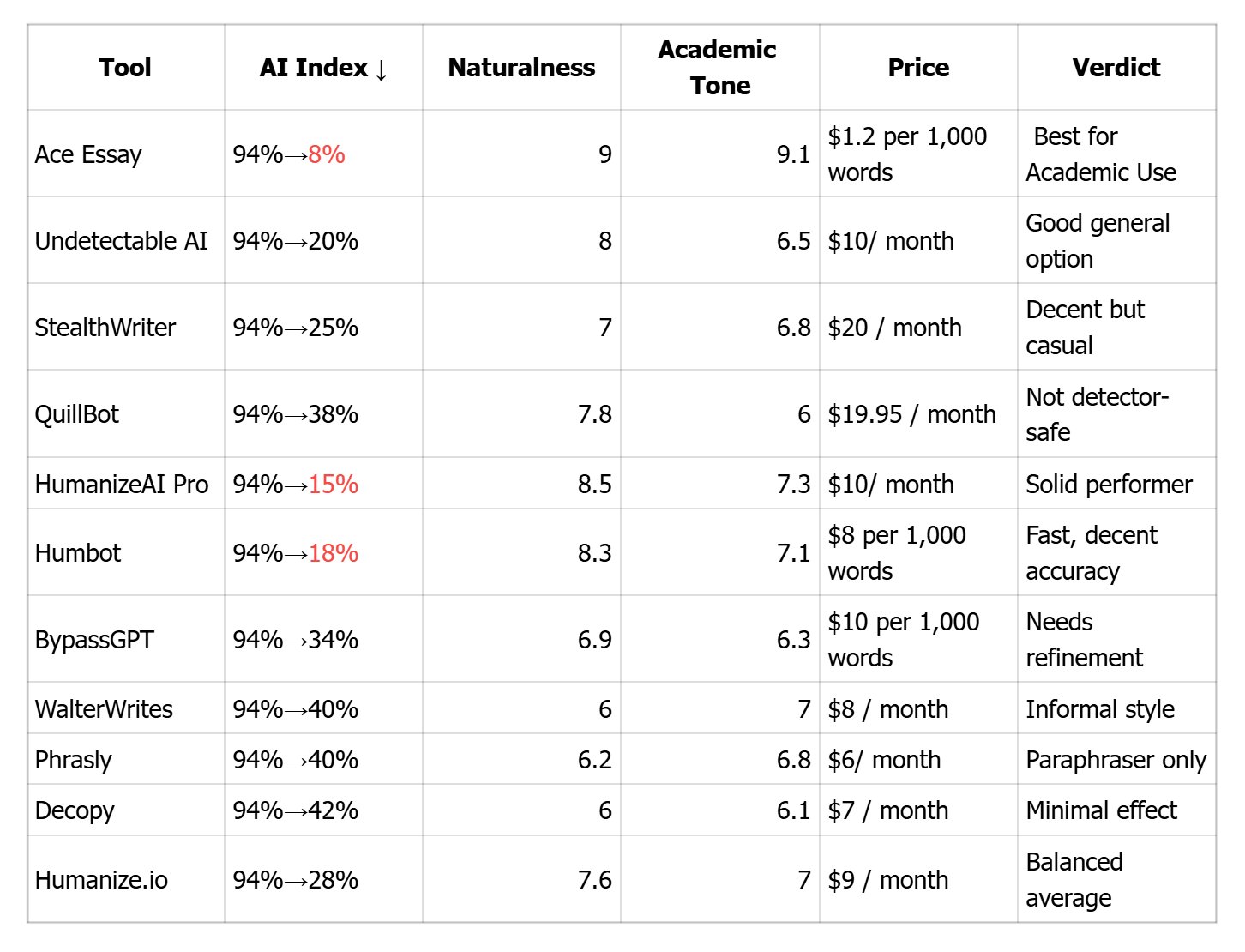
1.Ace Essay
Website: aceessay.ai
Score:9.1 / 10
Naturalness: 9.0 | Academic Coherence: 9.1 | AI Index after processing: ↓ from 94% → 8%
Price: $1.2 per 1,000 words
Pros:
✅ Academic-specific model tuned for essay and thesis writing
✅ High accuracy in preserving citations and logical structure
✅ Multilingual interface (English, Chinese, Japanese, Korean…..)
✅ The revised text has a high degree of semantic consistency with the original text.
Cons:
⚠️Slight delay when processing long documents (>2,000 words)
2.Undetectable AI
Website: undetectable.ai
Score: 7.6 / 10
Naturalness: 8.0 | Academic Coherence: 6.5 | AI Index: ↓ from 94% → 20%
Price: $9.99 / month (Starter Plan)
Pros:
✅ Moderate success rate on Turnitin / GPTZero reduction
✅ Affordable monthly pricing and browser-based tool
✅ Good for light edits or short reports
Cons:
⚠️ Weak academic tone — risks making essays sound too conversational
⚠️ Tends to break structured argumentation in research papers
⚠️ Citation formatting often lost or altered
3.StealthWriter
Website:stealthwriter.ai
Score: 7.2 / 10
Naturalness: 7.0 | Academic Coherence: 6.8 | AI Index: ↓ from 94% → 25%
Price: $20 / month (Basic Plan)
Pros:
✅ Good natural rhythm for casual or narrative text
✅ Handles medium-length text (500–1500 words) efficiently
Cons:
⚠️ Casual tone unsuitable for university essays
⚠️ Formatting loss (citations, indentation) in output
⚠️ High-tier plans costlier than competitors with similar performance
4.QuillBot
Website: quillbot.com
Score: 6.9 / 10
Naturalness: 7.8 | Academic Coherence: 6.0 | AI Index: ↓ from 94% → 38%
Price: $19.95 / month
Pros:
✅ Reliable paraphrasing engine with grammar tools
✅ Browser extensions and Google Docs integration
✅ Good for minor style adjustments
✅ Stable and easy to use
Cons:
⚠️ Weak AI detection evasion ability
⚠️ Often flattens sentence complexity
⚠️ Subscription cost relatively high
5.HumanizeAI Pro
Website: humanizeai.pro
Score: 8.1 / 10
Naturalness: 8.5 | Coherence: 7.3 | AI Index: ↓ from 94% → 15%
Price: $10 / month
Pros:
✅ High fluency and natural rhythm
✅ Effective at lowering GPTZero detection rates
✅ Quick rewriting speed
Cons:
⚠️ Citation and reference list formatting issues
⚠️ Slight meaning drift on long sentences
⚠️ Occasional redundancy in phrasing
6.WalterWrites
Website: walterwrites.ai
Score: 6.8 / 10
Naturalness: 6.0 | Coherence: 7.0 | AI Index: ↓ from 94% → 40%
Price: $8 / month
Pros:
✅ Simple interface and quick processing
✅ Suitable for blog or narrative text
✅ Low monthly cost
Cons:
⚠️ Weak academic tone
⚠️ Minimal AI-rate improvement
⚠️ Frequent loss of structure in academic drafts
7.Humbot
Website: humbot.ai
Score: 7.9 / 10
Naturalness: 8.3 | Coherence: 7.1 | AI Index: ↓ from 94% → 18%
Price: $8 per 1,000 words
Pros:
✅ Competitive pricing
✅ Stable AI score reduction
✅ Natural linguistic rhythm
✅ Suitable for humanities coursework
Cons:
⚠️ Minor grammar inconsistencies
⚠️ No reference formatting function
⚠️ Not ideal for very long research papers
8.BypassGPT
Website: bypassgpt.io
Score: 6.7 / 10
Naturalness: 6.9 | Coherence: 6.3 | AI Index: ↓ from 94% → 34%
Price: $10 per 1,000 words
Pros:
✅ Modern and intuitive interface
✅ Acceptable speed
✅ API support
Cons:
⚠️ Overly aggressive rewriting
⚠️ Average AI rate reduction
⚠️ Meaning shifts on complex arguments
9.Phrasly
Website: phrasly.ai
Score: 6.5 / 10
Naturalness: 6.2 | Coherence: 6.8 | AI Index: ↓ from 94% → 40%
Price: $6 / month
Pros:
✅ Budget-friendly
✅ Simple and quick interface
✅ Decent for casual rewriting
Cons:
⚠️ Simplifies complex structures
⚠️ Unsuited for academic writing
10.Decopy
Website: decopy.ai
Score: 6.3 / 10
Naturalness: 6.0 | Coherence: 6.1 | AI Index: ↓ from 94% → 42%
Price: $7 / month
Pros:
✅ Low-cost subscription
✅ Fast output speed
✅ Lightweight and easy to use
Cons:
⚠️ Frequent truncation and grammar errors
⚠️ Little AI-rate improvement
⚠️ Lacks academic tone or structure
11.Humanize.io
Website: humanize.io
Score: 7.4 / 10
Naturalness: 7.6 | Coherence: 7.0 | AI Index: ↓ from 94% → 28%
Price: $9 / month
Pros:
✅ Simple, stable rewriting
✅ Consistent AI reduction
✅ Reliable grammar correction
Cons:
⚠️ Over-neutral tone
⚠️ Weak in argumentative writing
⚠️ Limited academic adaptation
In conclusion
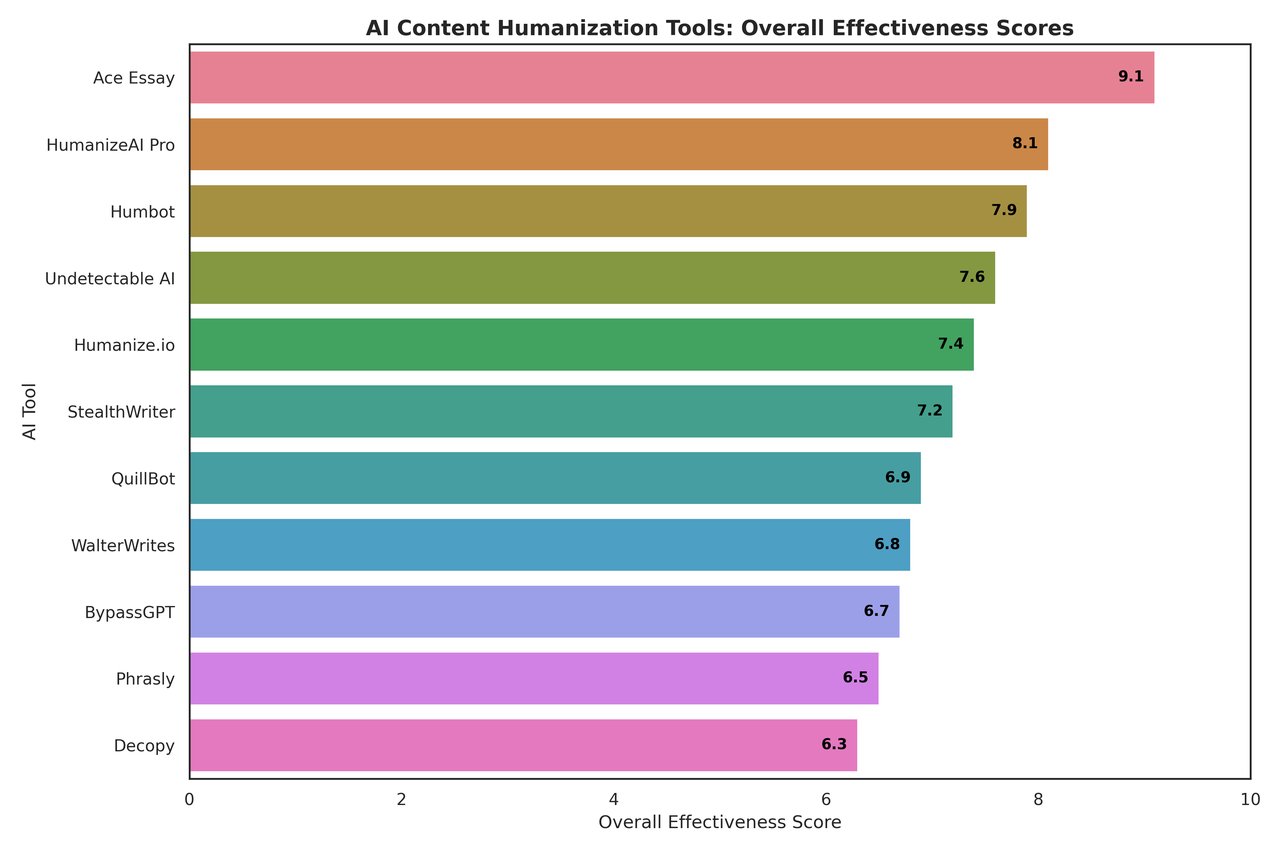
Through this test, we found that most “AI humanizers” still fail to handle academic nuance — often flattening argumentation or simplifying tone. Well, logically structured papers with linguistic naturalness would be the strongest output from Ace Essay. QuillBot or Phrasly is suggested for more general paraphrasing; however, they struggle with AI detectability.
This mainly requires the demand of choosing appropriate tools according to different scenarios.
- In drafting an essay on a Literary and Humanities-related topic: Use ChatGPT or Claude for initial ideas → run through Ace Essay to humanize tone and reduce AI rate → final polish it in QuillBot
- Quick AI-Lowering for Coursework:Undetectable AI / Humbot + Ace Essay → These tools can give a fast first pass, but Ace Essay adds the academic depth needed for formal submission.
- Budget or Fast Tasks:Humbot / Phrasly /Humanize.io + Ace Essay → These lighter tools help for quick edits or drafts; Ace Essay can be used at the end for quality assurance.
At last, it is important to note that AI humanizers are not “cheating tools.” Academic humanizers are not designed to falsify authorship or bypass integrity systems. Their proper use lies in:
- improving linguistic naturalness of AI drafts;
- refining non-native writing into idiomatic academic English;
In short: A humanizer should enhance clarity — not conceal authorship.
You can access Aceessay’s Bypass Turnitin page to try the Aceessay leading humanization technology.
About the Author
Claire Dawson is a dynamic content strategist at AceEssay, blending creativity with data-driven insights to craft compelling narratives and optimize SEO strategies. With a solid background in Marketing and Digital Media, Claire thrives on helping brands, especially in the academic space, grow their digital presence.